Velveeta is a pasteurised process cheese product that is produced by Kraft Foods in the United States of America. Its popularity has grown exponentially from its first launch in 1918. But is Velveeta actually good for you? Read on to discover the nutrition facts for Velveeta.

SEE ALSO: Nutrition facts for popular world cheeses in The Cheese Wanker’s index →
What is Velveeta?
Velveeta is, in essence, a processed cheese product renowned for its exceptional smoothness and versatility. Crafted through a meticulous blend of natural cheeses, emulsifiers, and other additives, Velveeta undergoes a precise processing method that results in its distinctive creamy texture and melting properties.
Unlike natural cheeses that age and develop distinct flavours, Velveeta undergoes a process where the cheese proteins are broken down, yielding a smooth consistency. This meticulous processing not only grants Velveeta its unique texture but also provides it with an extended shelf life compared to traditional cheeses.
The blend of various cheese types ensures that Velveeta strikes a balance between rich, savoury flavours and a luxurious, creamy feel on the palate.
One of Velveeta’s defining features is its unparalleled versatility in the kitchen. Its smooth, velvety texture makes it an ideal base for dips, sauces, soups and casseroles. Its exceptional melting properties mean it can transform even the simplest of dishes into a culinary delight.
Whether used to create a gooey, indulgent Macaroni & Cheese or a luscious queso dip, Velveeta’s adaptability has made it a favourite ingredient in households and restaurants alike.
Nutrition fact sheet
Country of origin
United States of America
Type of Cheese
Pasteurised Process Cheese Product
Milk
Cow
Examples
Velveeta Shells & Cheese, Cheesy Bites, Macaroni & Cheese, Cheesy Skillets
Benefits
Moderate Protein Content, Moderate to High Calcium Content
Considerations
Milk Protein Intolerance, Moderate to High Saturated Fat Content, Moderate to High Lactose Content, Excessively High Sodium Content, Not Recommended in Pregnancy
Nutrition review for Velveeta
Eating healthy plays a pivotal role in maintaining overall well-being and preventing chronic diseases. A balanced and nutritious diet provides our bodies with essential vitamins, minerals, and macronutrients, fuelling optimal physical and cognitive function.
With this in mind, let’s have a look at some of the key nutrition facts for Velveeta.
Calorie count
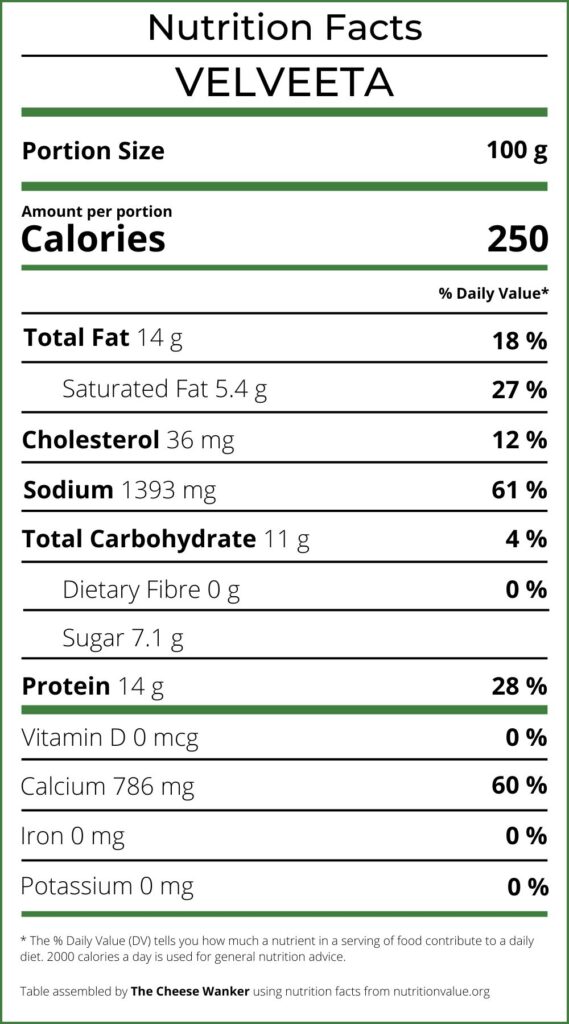
With 250 calories per serving, Velveeta might raise eyebrows among health-conscious consumers.
However, the calorie count alone doesn’t depict a food’s nutritional value accurately. Modern nutrition focuses on the source of calories rather than their mere quantity. A balanced diet considers the quality of fats, proteins and other nutrients, emphasising overall health and well-being.
Fat content
A critical aspect of Velveeta’s nutritional profile lies in its fat content, which comprises a substantial portion of the cheese product. Among the fats present, a notable concern is the elevated levels of saturated fats.
Saturated fats are a type of fat that can be found in various foods, including dairy products like Velveeta. While our body needs some saturated fats for essential functions such as hormone production and cell membrane structure, excessive consumption can lead to adverse health effects.
Unlike unsaturated fats, which are considered heart-healthy in moderate amounts, high intake of saturated fats has been linked to an increased risk of cardiovascular diseases. These fats can raise levels of LDL cholesterol, often referred to as “bad” cholesterol, which can clog arteries and lead to heart problems.
In the case of Velveeta, the high saturated fat content, which contributes to its creamy texture and rich taste, should be approached with caution. With 14 grams of total fat per serving, a significant portion of this fat comes from saturated fats.
Regular and excessive consumption of Velveeta, therefore, can contribute to exceeding the recommended daily intake of saturated fats, potentially leading to health issues over time.
You can learn more about the different types of fat in cheese and which cheeses have the lowest fat content here.
Protein content
Protein is a fundamental nutrient, serving as the building blocks of life, essential for muscle repair, growth and overall body function. In the case of Velveeta, while it contains a decent amount of protein, it’s worth noting that its protein content is notably lower compared to real, unprocessed cheese.
With 14 grams of protein per serving, Velveeta offers a moderate protein content. However, this amount pales in comparison to the protein content found in natural cheeses. Real cheese varieties generally provide a higher protein yield due to their minimal processing, retaining more of the natural proteins present in the original dairy sources.
For individuals seeking to boost their protein intake, especially athletes, bodybuilders or those with specific dietary requirements, opting for natural cheeses might be a more effective strategy.
Want to find out which cheeses have the highest protein content? Click here for our blog post covering cheeses with the highest protein content.
Cholesterol content
Cholesterol, a waxy substance found in every cell of the body, plays a vital role in building cell membranes and hormones. Velveeta, like many dairy products, contains cholesterol. However, the presence of cholesterol in food has often been a topic of concern and misconception.
For years, dietary cholesterol was vilified, with the assumption that high cholesterol foods directly lead to elevated blood cholesterol levels. Modern research, however, paints a more complex picture. While excessive consumption of cholesterol-rich foods can impact some individuals, dietary cholesterol isn’t the primary culprit behind high blood cholesterol levels.
Velveeta contains 36 mg of cholesterol per serving, a relatively moderate amount. In the context of a balanced diet and healthy lifestyle, this cholesterol content is unlikely to have a significant impact on most individuals’ cholesterol levels.
It’s essential to consider the overall dietary pattern, including the types of fats consumed, physical activity levels and genetics, when assessing the impact of Velveeta’s cholesterol content.
You can learn more about the impact of dietary cholesterol on blood cholesterol levels in our dedicated post here.
Salt content
Salt, a fundamental seasoning, has a transformative power over taste. It enhances flavours, adding depth and complexity to dishes. In the case of Velveeta, salt isn’t merely a component; it’s a defining characteristic, contributing significantly to its taste profile.
However, the remarkably high salt content in Velveeta raises concerns about its impact on health and well-being. Velveeta contains a staggering 1393 mg of sodium per serving, significantly surpassing the daily recommended intake.
Excessive sodium intake is associated with hypertension, cardiovascular diseases and kidney issues. Individuals with specific health conditions, such as high blood pressure, need to be particularly mindful of their sodium intake, as foods like Velveeta can significantly contribute to exceeding their recommended daily sodium limit.
You can read more about why salt is important in cheesemaking in our comprehensive post here.
Calcium content
Calcium as a mineral is synonymous with bone health and overall bodily functions. It’s a nutrient predominantly associated with dairy products. While Velveeta is a processed cheese product, it surprisingly boasts a relatively high calcium content.
Adequate calcium intake is crucial for individuals of all ages, ensuring the proper functioning of these essential bodily processes. In this context, foods rich in calcium, like Velveeta, offer a convenient way to supplement this vital nutrient in our diet.
Velveeta contains 786 mg of calcium per serving, a surprising figure considering its processed nature. While Velveeta includes non-dairy ingredients, the fortification process likely contributes significantly to its calcium content.
Incorporating Velveeta into one’s diet can be a pragmatic choice, especially for those with specific dietary constraints. While it offers a convenient calcium source, it’s crucial to balance its consumption with a variety of other calcium-rich foods, such as leafy greens and nuts.
Get our complete guide to calcium content in cheese in this post here.
Safety in pregnancy
Pregnancy is a time when dietary choices bear significant consequences for both the mother and the developing foetus. Velveeta does carry a relatively low risk of listeriosis, a foodborne illness that can be particularly harmful during pregnancy.
While Velveeta may pose a lower listeriosis risk, its nutritional profile raises red flags for expectant mothers. The high salt content is particularly concerning during pregnancy. Excessive sodium intake can lead to increased blood pressure, posing risks to both the mother and the developing baby.
Additionally, Velveeta’s processed nature raises questions about the quality of nutrients it provides, which is essential for the optimal development of the foetus.
Opting for natural, unprocessed dairy options like Cheddar or Gouda ensures that expectant mothers receive the necessary nutrients without compromising their health or the health of their unborn child.
Of course, if you’re unsure of what you can eat during pregnancy, you should consult your healthcare professional to get a personalised plan. You can read more about which cheeses you can eat when you’re pregnant by clicking here.
Lactose content
Lactose intolerance is a prevalent condition where the body lacks the enzyme lactase, necessary for breaking down lactose in the digestive system. As a result, individuals with lactose intolerance experience digestive discomfort, such as bloating, gas and diarrhoea, after consuming lactose-containing foods.
Velveeta contains higher lactose levels than most real cheeses due to its processing methods and ingredients. While some lactose-intolerant individuals might tolerate small amounts of lactose, Velveeta’s comparatively higher lactose content could trigger discomfort in those with even mild lactose sensitivity.
For those with lactose intolerance, opting for real cheeses with lower lactose content or lactose-free dairy alternatives is a safer choice. Lactose-free products have the lactose removed, allowing individuals to enjoy the taste and texture of dairy without the discomfort.
Being aware of one’s lactose tolerance level and choosing suitable alternatives ensures that individuals with lactose intolerance can still enjoy dairy-based products without compromising their digestive health.
Conclusion
In the world of processed foods, Velveeta cheese stands as a unique yet controversial choice. Understanding its nutritional profile unveils a complex tapestry of components, each with its own impact on our health.
In our exploration, we’ve uncovered the nuances of Velveeta’s nutritional content. While it provides certain essential nutrients like calcium and protein, its high levels of saturated fats, sodium and lactose raise concerns, particularly for individuals with specific health conditions.
In the vast landscape of food science, Velveeta serves as a reminder that every bite we take impacts our well-being. By being aware, by choosing wisely, we craft a diet that nurtures not just our taste buds, but also our health.
So, as you navigate the world of processed foods, including Velveeta in your culinary repertoire, remember the picture its nutrition facts paint. Armed with this knowledge, we can savour our meals, knowing that we’ve made choices that harmonise taste and health.
References
Overall nutritional content
The nutritional content of cheese in our table comes from the USDA Food Data Central Repository and cheese manufacturers. We realise that there can be variations between different brands and producers. Hence, the numbers we have used are averages.
Fat content
Our fat RDI data comes from Cleveland Clinic’s Healthy Fat Intake resource.
Type of fat in cheese as per Harvard T.H. Chan’s The Nutrition Source.
Protein content
Our protein RDI data comes from Harvard Medical School’s Harvard Health Publishing.
Cholesterol content
Is There a Correlation between Dietary and Blood Cholesterol? Evidence from Epidemiological Data and Clinical Interventions? – Maria Luz Fernandez and Ana Gabriela Murillo
Saturated fat, carbohydrate, and cardiovascular disease – Patty W Siri-Tarino, Qi Sun, Frank B Hu and Ronald M Krauss
Effect of cheese consumption on blood lipids: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials – Janette de Goede, Johanna M Geleijnse, Eric L Ding, Sabita S Soedamah-Muthu
Safety in pregnancy
All the advice relating to what cheeses you can eat during pregnancy in this article is based on the recommendations by health authorities in Australia, the UK and the USA. If you are unsure about what you can or cannot eat, please consult your doctor.
Australia – FSANZ, United Kingdom – NHS and United Sates of America – FDA
Lactose content
Lactose residual content in PDO cheeses
Detection of lactose in products with low lactose content
The analysis of lactose in milk and cheese products by HPLC
Food Standards ANZ Food Composition Database
Lactose & Galactose content of cheese