Comté is a remarkable cheese originating from the beautiful region of Jura. Known for its rich flavour and distinctive characteristics, this mountain cheese has gained popularity worldwide. In this blog post, we delve into the nutrition facts of Comté, examining its composition and health benefits.

SEE ALSO: Nutrition facts for popular world cheeses in The Cheese Wanker’s index →
What is Comté?
Comté is a semi-hard cheese made from unpasteurised cow’s milk. The production process involves careful craftsmanship, ensuring that the cheese attains its exceptional taste and texture.
Comté cheese is aged for a minimum of four months, but it can be aged for up to 24 months, intensifying its flavours and developing unique aromas.
Nutrition fact sheet
Nutritional review for Comté
Eating healthy plays a pivotal role in maintaining overall well-being and preventing chronic diseases. A balanced and nutritious diet provides our bodies with essential vitamins, minerals, and macronutrients, fuelling optimal physical and cognitive function.
With this in mind, let’s have a look at some of the key nutrition facts for Comté.
Lactose Intolerance
Firstly, Comté is a favourable choice for individuals with lactose intolerance. Lactose, the naturally occurring sugar in milk, undergoes a significant transformation during the cheesemaking process.
As a result, Comté cheese contains only trace amounts of lactose, making it easier to digest for those with lactose intolerance. Therefore, lactose-intolerant individuals can enjoy the savoury delights of Comté without experiencing discomfort.
Fat Content
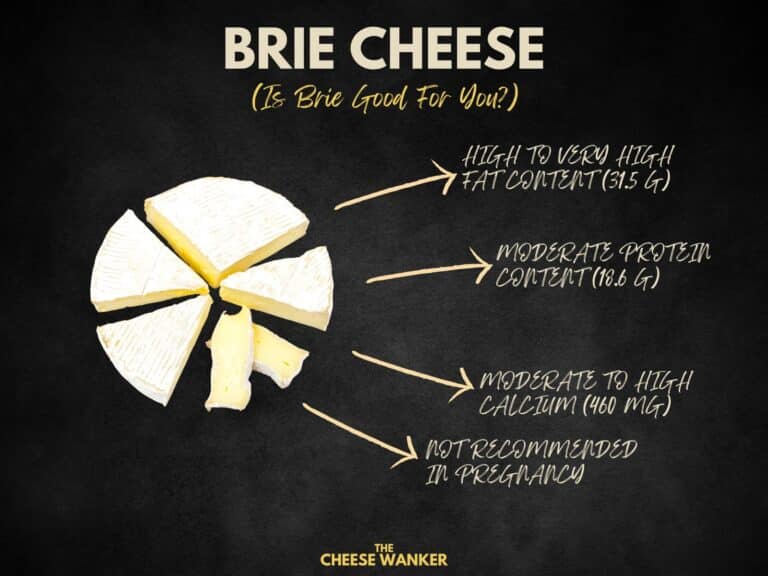
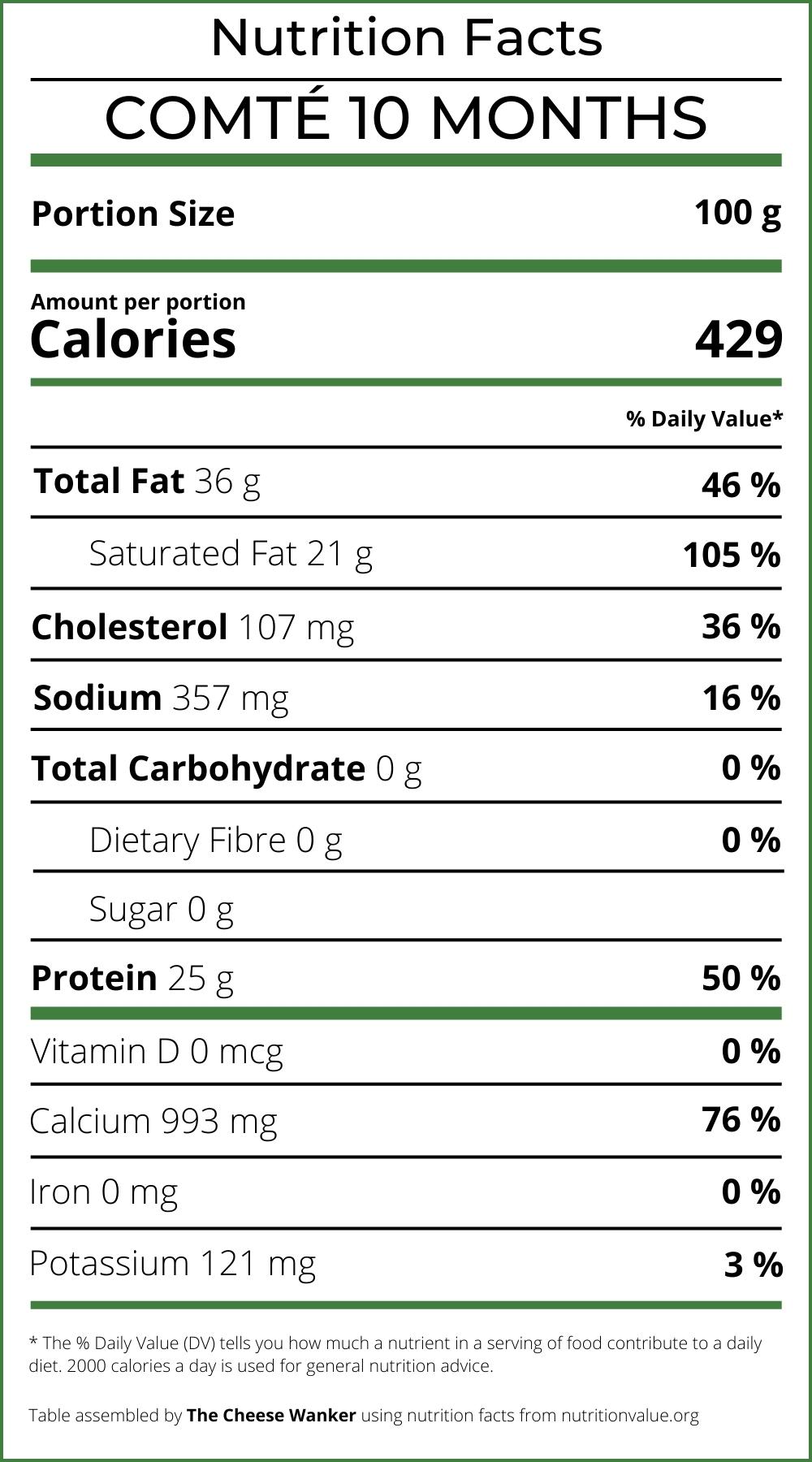
Besides, Comté boasts a moderate fat content, contributing to its luscious texture and delightful taste. With an average fat content of 36%, this cheese provides a satisfying mouthfeel.
Furthermore, the presence of fat enables better absorption of fat-soluble vitamins, such as vitamin A, D, E and K. While it is important to consume fats in moderation, the fat content in Comté adds to its nutritional profile, making it a wholesome choice for cheese enthusiasts.
You can learn more about the different types of fat in cheese and which cheeses have the lowest fat content here.
Cholesterol Content
Comté, despite its deliciousness, does contain a moderate amount cholesterol. However, research has shown that dietary cholesterol has a limited impact on blood cholesterol levels compared to saturated and trans fats.
When consumed as part of a balanced diet, the cholesterol content in Comté is unlikely to adversely affect your cardiovascular health. As with any food, moderation is key to maintaining a healthy diet.
Protein Content
Protein is an essential macronutrient vital for various bodily functions, including muscle growth, repair, and immune system support.
With approximately 25 grams of protein per 100 grams, Comté contributes significantly to your daily protein requirements. Incorporating this cheese into your diet can be particularly beneficial for individuals following a meat-free or low-meat diet.
Want to find out which cheeses have the highest protein content? Click here for our blog post covering cheeses with the highest protein content.
Safety in Pregnancy
Pregnant women often seek guidance on safe food choices to ensure a healthy pregnancy. Comté cheese can be safely consumed during pregnancy, even though it is made with raw milk.
Its prolonged maturation process reduces its moisture content and eliminates any harmful bacteria. As a result, pregnant women can safely enjoy Comté as a table cheese. And, of course, they can savour it cooked or melted in a warming dish.
Of course, if you’re unsure of what you can eat during pregnancy, you should consult your healthcare professional to get a personalised plan. You can read more about which cheeses you can eat when you’re pregnant by clicking here.
Salt Content
Being mindful of sodium intake is essential for maintaining a balanced diet. Compared to most cheeses, a 10-month-old Comté is relatively low in sodium and salt. Indeed, most versions of this cheese only contain around 300-400 mg of sodium per 100 g.
You can read more about why salt is important in cheesemaking in our comprehensive post here.
Calcium Content
Notably, Comté is also an excellent source of calcium, a vital mineral essential for bone health and proper functioning of the nervous system. With approximately 1,000 mg of calcium per 100 grams, Comté can significantly contribute to your daily calcium requirements.
Incorporating this cheese into your diet can be particularly beneficial for individuals who may have difficulties obtaining sufficient calcium from other sources.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Comté offers a delightful combination of taste and nutrition. With its moderate fat, ample protein and abundant calcium, Comté presents a viable option for those seeking a healthy and flavourful addition to their diet.
Furthermore, pregnant women can safely enjoy Comté even though it is made from raw milk. However, as with any food, moderation is key to achieving a balanced and wholesome diet.
What’s your favourite age for Comté? Drop us a comment below to join the conversation.
References
Overall nutritional content
The nutritional content of cheese in our table comes from the USDA Food Data Central Repository, the Australian Food Composition Database and cheese manufacturers. We realise that there can be variations between different brands and producers. Hence, the numbers we have used are averages.
Fat content
Our fat RDI data comes from Cleveland Clinic’s Healthy Fat Intake resource.
Type of fat in cheese as per Harvard T.H. Chan’s The Nutrition Source.
Protein content
Our protein RDI data comes from Harvard Medical School’s Harvard Health Publishing.
Cholesterol content
Is There a Correlation between Dietary and Blood Cholesterol? Evidence from Epidemiological Data and Clinical Interventions? – Maria Luz Fernandez and Ana Gabriela Murillo
Saturated fat, carbohydrate, and cardiovascular disease – Patty W Siri-Tarino, Qi Sun, Frank B Hu and Ronald M Krauss
Effect of cheese consumption on blood lipids: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials – Janette de Goede, Johanna M Geleijnse, Eric L Ding, Sabita S Soedamah-Muthu
Safety in pregnancy
All the advice relating to what cheeses you can eat during pregnancy in this article is based on the recommendations by health authorities in Australia, the UK and the USA. If you are unsure about what you can or cannot eat, please consult your doctor.
Australia – FSANZ, United Kingdom – NHS and United Sates of America – FDA
Lactose content
Lactose residual content in PDO cheeses
Detection of lactose in products with low lactose content
The analysis of lactose in milk and cheese products by HPLC
Food Standards ANZ Food Composition Database
Lactose & Galactose content of cheese